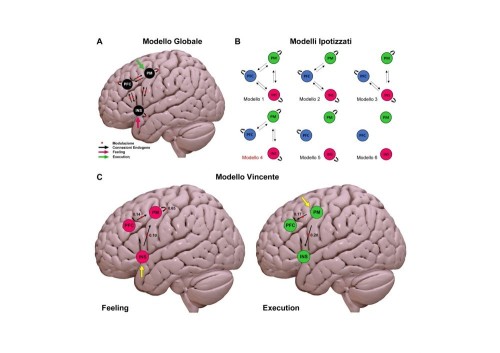
A typical 2-gram silicon chip requires 1.6 kilograms of fossil fuel, 72 grams of chemicals and 32 kilograms of water to manufacture, according to a new estimate.
In other words, behind those innocuous and almost weightless slivers of silicon in our 'phones, computers and domestic appliances lies a mountain of other materials, some of which are far from friendly to the environment.
The study, carried out by Eric Williams, of the United Nations University in Tokyo, and his colleagues, doesn't imply that microchips are a bad thing. After all, the smaller the chip, the less material is needed to house it - witness the shrinking personal computer. Smarter electronic devices also use energy more efficiently.
But, it suggests, efforts to make environmentally friendly chips should concentrate on reducing the energy needed to manufacture them, rather than making chips run on less power.
Data on chips
Williams's team gathered data from a United Nations Environment Programme technical report, a report by the US-based Microelectronics and Computer Technology Corporation, and an anonymous electronics firm1.
They totted up all of the chemicals, including fossil fuels, involved in transforming raw quartz - silicon dioxide, usually in the form of sand - into a 32-MB RAM microchip.
To make the high-grade silicon needed for the chips requires 160 times the energy used to produce raw silicon. This accounts for about half of the total energy used by the chip. Only a quarter is consumed during its processing life.
And because a chip's components are so tiny and precisely engineered, far more materials, such as fuels and solvents, are needed for their manufacture than for more traditional goods.
The mass of these secondary materials outweighs the product by a factor of 600. In contrast, making a typical car requires only about twice its weight in fossil fuels.
Industries have long been conscious of their products' material cost. They assess environmental impacts in terms of what happens to products at the end of their lives and the resources needed to make and to use them.
But such analyses are rare for semiconductors, say Williams and colleagues. It's known that some of the chemicals used to make chips, such as the solvents called polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), are toxic - but the environmental costs of apparently innocent materials such as water are less clear.
References
# Williams, E. D., Ayres, R. U. & Heller, M. The 1-7 kilogram microchip: energy and material use in the production of semiconductor devices. Environmental Science and Technology, Published online, doi:10.1021/es025643o (2002). |Article|
Ultimi Articoli

Se ne va Valentino, l'ultimo imperatore della moda mondiale
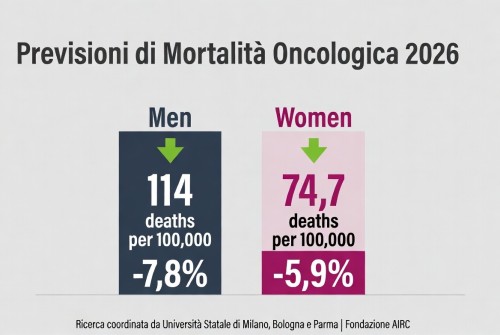
La mortalità per cancro cala in Europa – tassi in diminuzione nel 2026, ma persistono disparità

Carofiglio porta — Elogio dell'ignoranza e dell'errore — al Teatro Manzoni

Teatro per tutta la famiglia: “Inside and Out of Me 2” tra ironia e interazione

Dogliani celebra quindici anni di Festival della TV con “Dialoghi Coraggiosi”

Sesto San Giovanni — 180 milioni dalla Regione per l’ospedale che rafforza la Città della Salute

Triennale Milano — Una settimana di libri, musica, danza e arti sonore dal 20 al 25 gennaio

A febbraio la corsa alle iscrizioni nidi – Milano apre il portale per 2026/2027

Hackathon 2025 — a Palazzo Lombardia gli studenti sfidano il cyberbullismo